Difference between Earth and Mars
We are planning to migrate to a different planet, but we don't know how the Planet is different from ours. Let us find out the differences between our lovely planet earth and our next home Mars.
Earth vs Mars
Difference between Earth and Mars is a very hot topic as currently humans are exploring Mars to see whether it can support life. Earth and Mars are terrestrial planets that form part of our solar system. They are two different planets that show differences between them in terms of their characteristics and properties. The Earth is a planet that supports life better than Mars. This is due to the favorable living conditions it offers to the living beings by virtue of its acceptable distance from the sun. From among the planets in our solar system, Mars is the planet that resembles Earth the most though there are differences. That is why scientists are experimenting in creating colonies in Mars for humans to live. Mars is considered to be the Earth’s closest neighbor planet in the space.
More about Earth

Earth is the third planet from the Sun. Earth is situated at a distance of 149, 597, 891 kilometers (92, 955, 820 miles) from the Sun. The Earth spins or rotates on its axis from west to east. This rotation causes day and night. The Earth completes one rotation every 24 hours. As the earth rotates on its axis, it also revolves or moves around the Sun. The earth completes one revolution around the sun in about 365 days. This period of time is called as a year. The axis of Earth is tilted 23.5 degrees. The Earth experiences different seasons because the axis of the earth is tilted 23.5 degrees. As a result, when it goes around the Sun, the seasons change.The Earth has the moon as its natural satellite.
More about Mars

Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the red planet because of its colour, which is due to the rusty dust. With regard to the distance, the planet of Mars is situated at a distance of 227, 936, 637 kilometers (142, 633, 260 miles) from the Sun. The factor of light is also not conducive to life in the planet of Mars. The length of a day on Mars is 24 hours and 37 minutes. It takes 687 earth days for the planet of Mars to orbit the Sun. The axis of Mars is also slightly titled. It is tilted 25 degrees. Mars has two natural satellites or moons. They are Phobos and Deimos. The atmosphere of Mars contains Carbon Dioxide, Nitrogen, Argon, Oxygen, Water Vapor, and Nitric Oxide. About 95% is Carbon Dioxide. Oxygen is only about 0.13%, which is very low.
What is the difference between Earth and Mars?
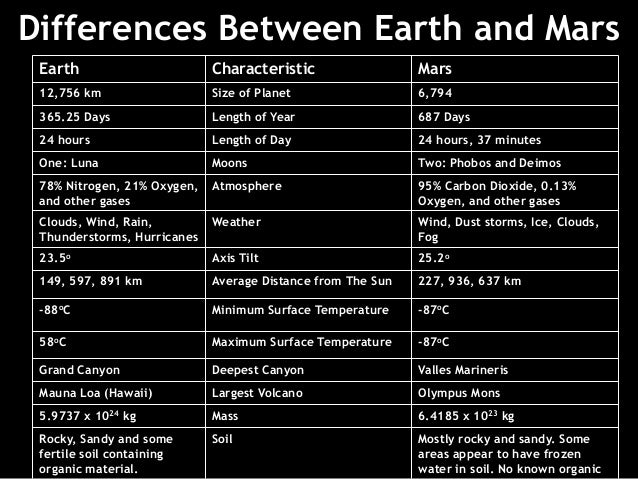
- Earth is the third planet from the Sun whereas Mars is the fourth planet from the sun.
- Earth is situated 149, 597, 891 kilometers (92, 955, 820 miles) from theSun. Mars is situated at a distance of 227, 936, 637 kilometers (142, 633, 260 miles) from the Sun.
- However, when it comes to size, Earth is almost twice the diameter of Mars. In other words, Earth is bigger than Mars. The diameter of the earth is 12, 742 km while that of mars is 6, 779 km.
- Earth takes 365 days to go around the Sun. Mars takes 687 earth days to go around the Sun. In other words, the period Mars takes to go round the Sun is greater than the period Earth takes to go round the Sun.
- As a result of Mars being situated further away from the Sun than the Earth, Mars is considered to be cooler than the Earth.
- The time a planet takes to make a full rotation on its axis is known as the length of day of a planet. A day on Earth is 24 hours. A day on Mars is 24 hours and 37 minutes.
- The axis of Earth is titled 23.5 degrees while the axis of Mars is titled 25 degrees.
- Earth has water on its surface. Mars, however, does not have liquid water.
- Both planets have moons or natural satellites. However, Earth has only one when Mars has two. The names of Martian moons are Phobos and Deimos.
- The atmosphere of Earth contains Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon and Carbon Dioxide. Nitrogen is in the highest amount and then oxygen. The atmosphere of Mars contains Carbon Dioxide, Nitrogen, Argon, Oxygen, Water Vapor and Nitric Oxide. About 95% is Carbon Dioxide. Oxygen is only about 0.13% which is very low.
- The gravity on Mars is about one third of the gravity on Earth.
Climate of Mars

The climate of Mars has been a topic of scientific curiosity for centuries, in part because it is the only terrestrial planet whose surface can be directly observed in detail from the Earth with help from a telescope.
Although Mars is smaller than the Earth, 11% of Earth's mass, and 50% farther from the Sun than the Earth, its climate has important similarities, such as the presence of polar ice caps, seasonal changes and observable weather patterns. It has attracted sustained study from planetologists and climatologists. While Mars' climate has similarities to Earth's, including periodic ice ages, there are also important differences, such as much lower thermal inertia. Mars' atmosphere has a scale height of approximately 11 km (36,000 ft), 60% greater than that on Earth. The climate is of considerable relevance to the question of whether life is or ever has been present on the planet. The climate briefly received more interest in the news due to NASA measurements indicating increased sublimation of one near-polar region leading to some popular press speculation that Mars was undergoing a parallel bout of global warming, although Mars' average temperature has actually cooled in recent decades, and the polar caps themselves are growing.
Martian soil

Martian soil is the fine regolith found on the surface of Mars. Its properties can differ significantly from those of terrestrial soil, including its toxicity due to the presence of perchlorates. The term Martian soil typically refers to the finer fraction of regolith. So far, no samples have been returned to Earth, the goal of a Mars sample-return mission, but the soil has been studied remotely with the use of Mars rovers and Mars orbiters.
On Earth, the term "soil" usually includes organic content. In contrast, planetary scientists adopt a functional definition of soil to distinguish it from rocks. Rocks generally refer to 10 cm scale and larger materials (e.g., fragments, breccia, and exposed outcrops) with high thermal inertia, with areal fractions consistent with the Viking Infrared Thermal Mapper (IRTM) data, and immobile under current aeolian conditions. Consequently, rocks classify as grains exceeding the size of cobbles on the Wentworth scale.
This approach enables agreement across Martian remote sensing methods that span the electromagnetic spectrum from gamma to radio waves. ‘‘Soil’’ refers to all other, typically unconsolidated, material including those sufficiently fine-grained to be mobilized by wind. Soil consequently encompasses a variety of regolith components identified at landing sites. Typical examples include: bedform armor, clasts, concretions, drift, dust, rocky fragments, and sand. The functional definition reinforces a recently proposed generic definition of soil on terrestrial bodies (including asteroids and satellites) as an unconsolidated and chemically weathered surficial layer of fine-grained mineral or organic material exceeding centimeter scale thickness, with or without coarse elements and cemented portions.
Soil Productivity
Although Mars is the most Earth like of our neighbouring
plantes.Mars and Earth differ in many ways.The surface temperature
of Mars is about -60 degree and it has a thin atmosphere primarily
made of carbon dioxide.
Unlike soil ,which is humid and rich in nutrients and
microorganisms that supports plants growthb,Mars is covered with
regolith . This is an arid material that contains perchlorate
chemicals that are toxic to humans.
Also despite the latest sub- surface lake find water on Mars
mostly exists in the form of ice ,and the low atmospheric pressure
of the planets makes liquid water boil at around 5 degree.
Plant on Earth have evolved for hundreds of millions of years and
are adapted to terrestrial condition, but they will not grow well
on Mars. This means that substantial resources that would be
scarce and priceless for humans on Mars ,like liquid water and
energy, would need to be allocated to achieve efficient farming by
artificially creating optimal plant growth condition.
Adapting plants to Mars
A more rational alternative is to used previous work has suggested
the use of microbes as a source of food on Mars . The use of
hydroponic greenhouse and controlled environmental system, similar
to one being tested onboard the International Space Station to
grow crops , is another option.
In the general Genes, we provide a new perspective based on the
use of advanced synthesis biology to improve the potential
performance of plants life on Mars . Synthetic biology is a fast -
growing field . It combines principle from engineering DNA
science, and computer science to impart new and improved function
to living organisms. Not only can weread DNA , but we can also
design biological system,test them,and even engineer whole
organisms. Yeast is just one example of industrial workshop
microbes whose whole genome is currently being re-engineered by an
international consortium.
Benefits for Earth
Developing the next generation of crops required for sustaining humans on Mars would also have great benefits for people on Earth . The growing global population is increasing the demand for food. To meet this demand we just increase agricultural negatively impacting our environment. The best way to achieve these goals would be to improve the crops that are already widely used. Setting up facilities such as the proposed Mars Biofoundary would bring immense benefits to the turnaround time of plants research with implications for food security and environmental protection. So ultimately, the main beneficiary of effort to develop crops for Mars would be Earth .
Volcanism on Mars

Volcanic activity, or volcanism, has played a significant role in the geologic evolution of Mars. Scientists have known since the Mariner 9 mission in 1972 that volcanic features cover large portions of the Martian surface. These features include extensive lava flows, vast lava plains, and the largest known volcanoes in the Solar System. Martian volcanic features range in age from Noachian (>3.7 billion years) to late Amazonian (< 500 million years), indicating that the planet has been volcanically active throughout its history, and some speculate it probably still is so today. Both Earth and Mars are large, differentiated planets built from similar chondritic materials. Many of the same magmatic processes that occur on Earth also occurred on Mars, and both planets are similar enough compositionally that the same names can be applied to their igneous rocks and minerals.
Volcanism is a process in which magma from a planet's interior rises through the crust and erupts on the surface. The erupted materials consist of molten rock (lava), hot fragmental debris (tephra or ash), and gases. Volcanism is a principal way that planets release their internal heat. Volcanic eruptions produce distinctive landforms, rock types, and terrains that provide a window on the chemical composition, thermal state, and history of a planet's interior.
Magma is a complex, high-temperature mixture of molten silicates, suspended crystals, and dissolved gases. Magma on Mars likely ascends in a similar manner to that on Earth. It rises through the lower crust in diapiric bodies that are less dense than the surrounding material. As the magma rises, it eventually reaches regions of lower density. When the magma density matches that of the host rock, buoyancy is neutralized and the magma body stalls. At this point, it may form a magma chamber and spread out laterally into a network of dikes and sills. Subsequently, the magma may cool and solidify to form intrusive igneous bodies (plutons). Geologists estimate that about 80% of the magma generated on Earth stalls in the crust and never reaches the surface.
Mars Base Camp
Mars Base Camp (MBC) is a crewed Mars laboratory orbiter concept under study that was commissioned by NASA from Lockheed Martin in US. It would use both future and proven concepts as well as the Orion MPCV, also built by Lockheed Martin.
The Mars Base Camp concept is being proposed to NASA as a possible version of the Deep Space Transport, a crewed interplanetary spacecraft to support science exploration missions to Mars of up to 1,000 days. It would be part of a larger architecture that includes the Lunar Gateway space station. As of April 2018, the Mars transit vehicle is still a concept to be studied, and NASA has not officially proposed the mission in an annual U.S. federal government budget cycle.
